Products and Varieties¶
Entries for product records are grouped into the following five sections:
- PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
- CLASSIFICATION
- DIMENSIONS
- LOCATOR CONTROLS
- NOTES AND MESSAGES
In each section, a rule line separates basic mode entries (above the line) from advanced entries (below the rule). The sections for LOCATOR CONTROLS and NOTES AND MESSAGES are available in advanced mode only.
Product Identification¶
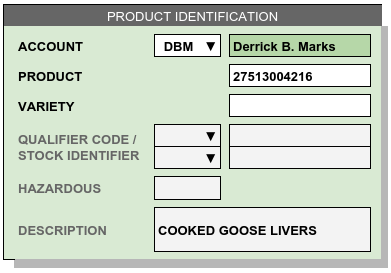
Required entries Account and Product, and optionally Variety, combine to form a unique identifier for each product. Other indexed entries which link to the product identifier for categories and search are included in this section: Stock Number alternatives, Description text, and a Hazard flag.
Tip
Special characters, spaces, or punctuation are not allowed in identifiers. These entries are limited to the 26 upper-case letters of ISO basic Latin alphabet along with numerals 0 through 9.
Basic Entries:¶
Account: Each product must be associated with an account. For private warehousing, this could be a department identifier or similar entry.
Product: A single alphanumeric entry will identify each tracked product. This entry should be used in reporting with the customer as well as in shipping and receiving documentation.
Variety: An optional adjunct of the product identifier can be used to distinguish between variants of a product which are reported together.
Tip
When creating new variety records of a base product, the Qualifiers, Hazardous, and Description entries will default to the values from the base product. Use unique packaging descriptions to distinguish between varieties. If there are only varieties of a product without a base record, no defaults will be generated.
Qualifiers and Stock Numbers: Each product may have several auxiliary identifiers such as a buyer code, UPC code, SKU number, and the like. These entries require qualifiers from the Product Identification Codes to categorize the associated identifiers.
Hazardous must be checked if a product requires DOT HAZMAT labeling.
Warning
Checking Hazard requires the Proper Shipping Name. In basic mode, a Hazard check will produce the warning message, This feature is available only in advanced mode.
Description text appears on shipping documents and other forms which members of the public are likely to read. Characters used in the description are not limited. Individual description words are indexed for searching products.
Advanced Entries:¶
- Packaging description spells out distinctive aspects of a particular product or variety. For example, “24/12 oz. cans” versus “6/48 oz. cans,” where either description represents a case with 288 ounces of product.
- Shipping Name is an alternative description specific to shipping documents such as the Bill of Lading. This entry is required for hazardous materials.
Product Classification¶
Products are classified according to WARES features or the conventions of warehousing and logistics.
Basic Entries¶
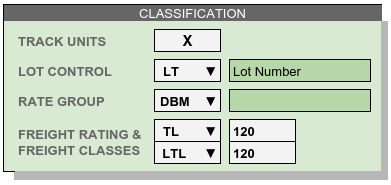
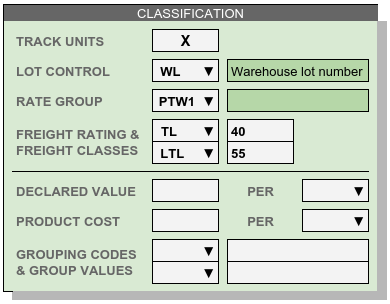
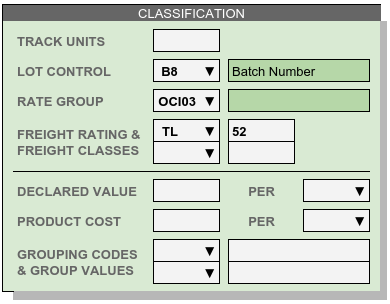
Lot Control Code specifies which piece of information may be required to use for a lot number. Other numbers tied to a lot or shipment should be included in receiving descriptions, or tracked with individual units. Once a Lot Control Code is selected, lot control numbers will be required on inventory transactions.
Products are considered fungible when Lot Control Code is left blank, and WARES will not maintain balances on individual lots of a fungible product. Control numbers will not be required on entry and inventory balance reporting will be summarized at the product level only.
Track Units Determines whether or not individual unit numbers will be required. Unit identifiers may be assigned to Individual odd units even if Track Units has not been required.
Rate Group identifies a set of rate records used in calculating the storage and handling fees for a group of products.
Freight Class specifies the classification system and transportation rating for a product. Classification systems include TL, LTL, and NMFC.
Carriers consider shipment bulk density, product durability, temperature control, and other factors when assigning a rate, but TL and LTL classes refer to density only. Carrier contracts may also specify a freight class, as when a carrier agrees to a single transportation rate for Freight All Kinds (FAK).
Advanced Entries¶
- Declared Value specifies the loss coverage per unit of product a customer requests for his goods under warehouse responsibility. Leave this entry blank when an account accepts the warehouse standard limitation of liability for negligence.
- Unit Cost or price is used to calculate rates for charges related to sales pricing.
- Grouping Code lists and values are optional codes for classifying and grouping products. These codes may be used in product selection or reporting filters.
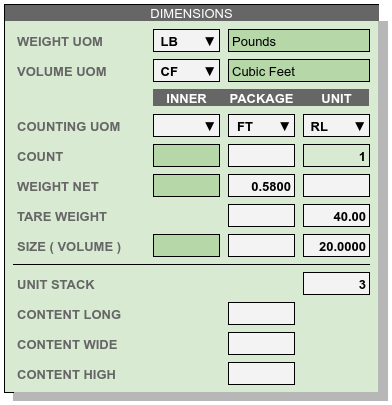
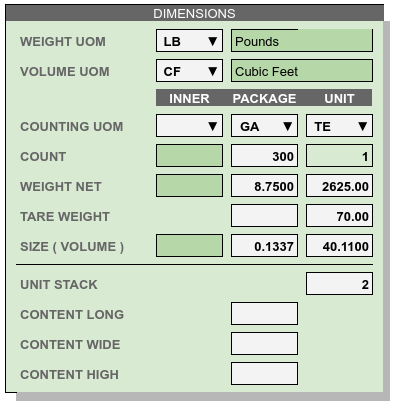
Product Dimensions¶
Dimension entries determine the uints of measure to display for goods, and the counts and factors to extend or extrapolate from weights, sizes, and counts of (inner or) packages entries up to unit inventory quantities and measures. Default values for a column are calculated once entries are made in the column preceding it (to its left).
Tip
Inner counts and measures, package linear dimensions, and unit stacking are not included in base mode.
Basic Entries¶
UOM: Each inventory level in a product SKU has a Unit Of Measure (UOM). For example, an item might come with 12 blister-pack eaches (EA) packed in each case (CA), and 64 cases stack on a pallet (PL). Then UOMs for the product would be INNER=EA, PACKAGE=CA, and UNIT=PL.
Tip
INNER UOM is optional in advanced mode, and if open-case picking will not happen, it should be left blank. Other entries in the INNER column are prohibited when the INNER UOM is blank.
Count represents the standard number of pieces which make up the next larger unit of inventory. In the previous example, a count of 12 blister-pack eaches make up one case, and a count of 64 cases comprise a pallet unit.
Weight: The weight of an inner piece, times the inner count, should equal the weight net of a package. The weights (Net + Tare) of a package times the package count should equal the weight net of a unit.
Tare Weight entries represent the extra packaging weight of packages, containers and shipping units.
Size tracks the volume of a piece or a container. Liquid sizes may be stated in gallons or liters, while dry sizes are usually expressed in cubic feet or cubic meters.
Advanced Entries¶
- Unit Stack determines the usage of location stack height. When a product is stored to a location, the minimum of the product’s unit stacking and the location’s stack height limit is used to calculate the location capacity.
- Package Long, Package Wide, and Package High are used when shipping via package carrier, where the carton dimensions are required.
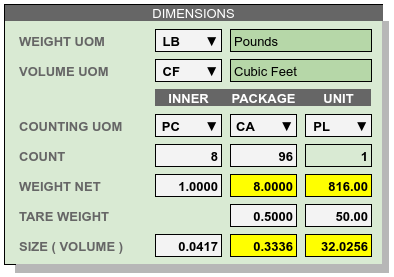
Dimensions Example¶
Six values (un-highlighted entries in the figure) must be entered to calculate from inner pieces to unit pallets, as shown in the following table.
| Entry Name | Entry Value | Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Inner Count | 8 | PC/CA |
| Inner Weight | 1.0000 | LB/PC |
| Inner Size | 0.0417 | CF/PC |
| Package Count | 96 | CA/PL |
| Package Tare | 0.5000 | LB/CA |
| Unit Tare | 50.00 | LB/PL |
Calculated default values are highlighted in the Dimensions example figure. The calculations and analysis of units is shown below.
| Default Entry | Calculation |
|---|---|
| Package Weight | 8 X 1.0 = 8.0
(PC/CA) X (LB/PC) = (LB/CA)
|
| Package Size | 8 X 0.0417 = 0.3336
(PC/CA) X (CF/PC) = (CF/CA)
|
| Unit Weight | 96 X (8.00 + 0.50) = 816.00
(CA/PL) X (LB/CA) = (LB/PL)
|
| Unit Size | 96 X 0.3336 = 32.0256
(CA/PL) X (CF/CA) = (CF/PL)
|
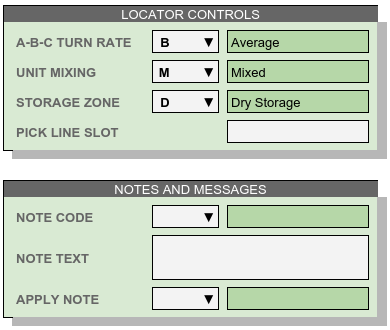
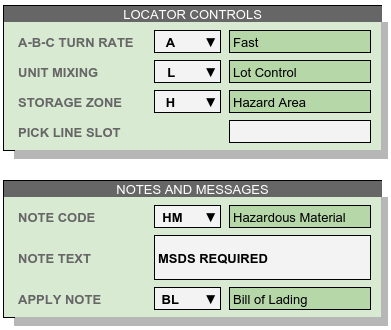
Locator Controls¶
Products interact with the Locator system through these settings, and through the Unit Stack dimension entry.
- A-B-C Turn Rate, or product velocity, describes how quickly products move through the warehouse.
- Unit Mixing indicates whether other products (for the same account) may be stored on the same pallet unit, or just packages of other lots.
- Storage Zone describes the warehouse area used to store this product. This entry could be a storage specification such as Dry/Cooler/Freezer, or it could refer to a warehouse area dedicated to the product’s account.
- Pick Line Slot specifies a location for picking individual pieces of a product.
Notes and Messages¶
Notes allow product information which is intended for clerical use, warehouse laborers, transportation, or recipient consumption to be recorded and then displayed on appropriate documents or other venues.
Note
The entirety of LOCATOR CONTROLS and NOTES AND MESSAGES are part of advanced mode.
Using Basic Mode¶
The nature of web pages makes data entry difficult for large forms, and this is particularly a problem on hand-held devices. Basic mode exists to reduce page sizes to a minimum while providing all commonly used features.
Basic mode displays only three form sections, with reduced entries. Basic dimensions were shown in the dimension example above; the Product Identification and Product Classification sections are shown below.