Building Locations¶
Locations Purpose¶
A Locator uses a list of places where goods may be stored in and around a warehouse building. These locations may include:
- Yards and Parking Lots
- Dock and Staging Areas
- Building and Room Divisions
- Aisles and Bays
- Pick Lines
- Mezzanines, Racks, Shelves
- Stationary and Moving Vehicles
The locator posts movements of goods into and out of locations, so that it can determine and direct the utilization of storage space.
Setup Facilities¶
Locations are defined in the context of a physical building or warehouse facility address. Before locations can be setup, an address record of type B for the building must be entered. Use the Add New Facility button to start a new facility record, or use Delected Selected to remove a building.
Editing a Facility Address¶
Click the pencil icon on a facility to edit the building address.
Note
The Edit (pencil) option on a facility should go straight to the Contacts update form, eliminating the intervening “New Facility” page.
Warehouse Layout¶
Click the layout icon to start defining building locations.
Before locations can be defined in software, the warehouse layout has to be determined. This will include calculations and measurements for the following:
- Dock door spacing
- Front staging area depth
- Aisle widths for turning
- Bay widths, depths, and height
- Number of aisles in warehouse
- Number of bays per aisle
- Rack storage area design
- Empty pallet exchange areas
- Column and overhead interferences
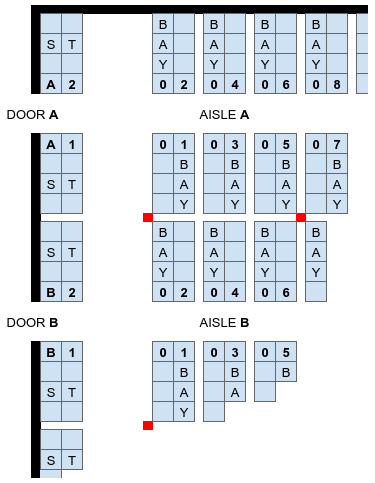
Part of a very basic warehouse layout schematic is shown in the sidebar. This Google Sheet shows how easily a building grid can be described, providing that the building is rectangular, the interior plan is regular, and there are few interferences.
For this example, the first building, building 1, might be described as:
| AREA | Feature | Code Start | Code End |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | DOOR | DOOR-A | |
| STAGING | STAGE-A-1 | STAGE-A-2 | |
| BAYS | A-01 | A-16 | |
| B | DOOR | DOOR-B | |
| STAGING | STAGE-B-1 | STAGE-B-2 | |
| BAYS | B-01 | B-16 | |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| L | DOOR | DOOR-L | |
| STAGING | STAGE-L-1 | STAGE-L-2 | |
| BAYS | L-01 | L-16 |
Setup Location Codes¶
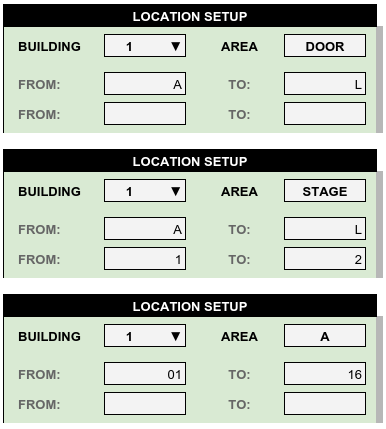
after the warehouse layout is determined, Location codes for a building can be setup on the Location Setup page. Location codes corresponding to the building shown above might be entered as follows:
| Feature | Code
Start
|
Code
End
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
| DOORS | DOOR-A | thru | DOOR-L |
| STAGING | STAGE-A-1 | thru | STAGE-L-2 |
| AISLE A | A-01 | thru | A-16 |
| AISLE B | B-01 | thru | B-16 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... |
| AISLE L | L-01 | thru | L-16 |
For this example, the sidebar presents possible location code definitions for all the doors and the adjacent staging areas right and left of the doors. Additional entries describe the storage bays on the right and left of aisles A through L.
Staging used two levels of ranges, configured to match the area letters A through L. WARES locator provides up to four ranges which may use either letters or numbers. For example, a rack area might have Area = RA, First Range 1 thru 8 (eight rack rows), second range 1 through 12 (twelve slots), and third range A through D (four shelf levels). This rack area would hold 384 pallets.
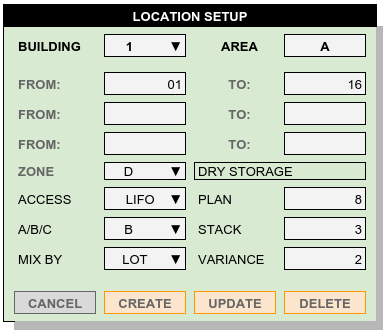
Location Setup Options¶
The Locator needs an accurate measure of capacity for each storage location. Use features described below to improve storage and labor efficiency, and to implement advanced capabilities such as directed inventory movement.
- ZONE – The warehouse company may zone a building into various areas, and specific customers or products can be restricted to applicable zones only. For example, the warehouse may have DRY and COOL zones, but also partitions for customers ADF and OCI. Locations within ADF and OCI partitions could be updated to reflect the associated zones. A default zone list is at Storage Zone.
- ACCESS – Determines the sequence of fill and retrieval for a location. In the previous layout example, the bay locations are LIFO because the first pallet placed in a bay will be the last to leave. However, Bays A-01 and B-02 back up to each other. Defining location AB-0102, where pallets are loaded from Aisle A and removed from aisle B, would provide FIFO storage – without restriping the floor. The Access options list is at Location Access Code.
- A/B/C – Locations can be rated by speed of access, from A to C. In the warehouse example, bays 1 through 6 might be A, 7 through 12 could be B, and 13 through 16 would then be C.
- MIX BY – Locations and pallets may be of the same lot, same date, same product, same account, or unrestricted. Setting Mix for a location will promote locations matching the requirements of products being stored. Mix options are listed at Unit / Location Mixing.
- PLAN, STACK, and VARIANCE – These three measures determine the storage capacity of a location. For our sample warehouse, the bays are eight pallets on the floor (Plan), with three pallets high (Stack), and no variance due to interference.
The Location Setup form creates, updates, or deletes multiple warehouse locations in a single step.
Warning
An update or deletion of locations in the setup will not affect location entries on existing product.
Locator Database Schema¶
Each warehouse location has a record in the Locations table. The database schema for Locations is found at LOCATIONS Data Table Columns.
Excluding location transfers, locator transaction lines are identically the inventory document line transactions. The database column layout for these transactions is available in documentation resources at LOT Lines Data Table Columns.